Pregnancy-Related Deaths: A Rising Concern in the U.S.
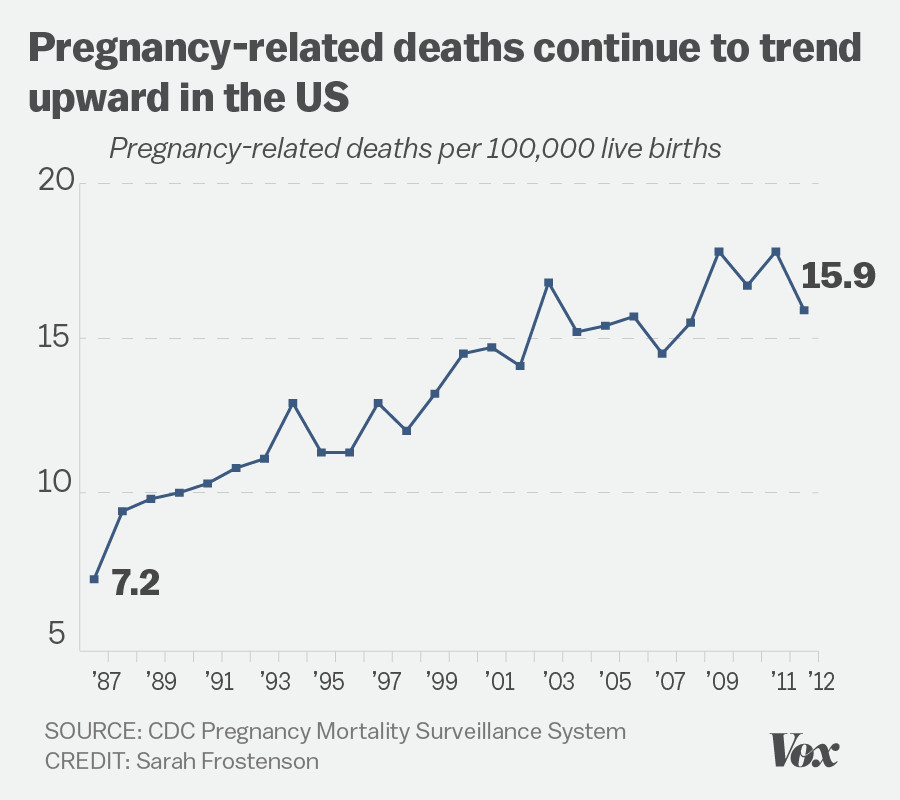
Pregnancy-related deaths have reached alarming levels in the United States, where the maternal mortality rate consistently outpaces that of other high-income countries. This surge in preventable deaths highlights the urgent need for better prenatal and postpartum care, as over 80% of these fatalities could have been avoided. Many factors contribute to these tragic outcomes, including significant racial disparities and the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases among pregnant individuals. Despite advancements in healthcare, systemic inequities and a fragmented healthcare system continue to hinder progress in reducing these numbers. Ending pregnancy-related deaths is not just a health issue; it is a matter of equity, requiring comprehensive policy reform and dedicated investment in maternal health services for all women.
The phenomenon of maternal mortality, often referred to in the context of pregnancy-related deaths, involves a range of tragic outcomes that can occur during and after childbirth. Despite advancements in medical care, the U.S. continues to grapple with high rates of these tragic incidents, revealing a pressing public health crisis. Key factors such as postpartum care, racial inequalities, and emerging health risks like cardiovascular disease significantly impact maternal health. The alarming rise in such preventable deaths calls for immediate attention to healthcare policies and practices. Understanding the underlying causes of these fatalities is essential for creating effective strategies to ensure safer pregnancies and healthier outcomes for all mothers.
Understanding Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
Pregnancy-related deaths in the United States highlight a disturbing trend: over 80% of these fatalities are preventable. Recent studies indicate that the U.S. leads high-income nations in maternal mortality rates, with these deaths increasing significantly from 2018 to 2022. This alarming data underscores a crucial need for enhanced maternal healthcare strategies, particularly focused on prenatal and postpartum care. Historically, these deaths are not just statistics; they reflect systemic issues within a fragmented healthcare system that often overlooks the fundamental needs of pregnant individuals.
The statistics surrounding pregnancy-related deaths reveal stark racial disparities and indicate that American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Addressing these disparities is crucial to ensuring equitable health outcomes for all communities. Moreover, the ongoing rise in pregnancy-related deaths necessitates an urgent call to action, emphasizing not just the need for immediate medical interventions but for long-term systemic health reforms that focus on improving healthcare access and quality for marginalized populations.
The Impact of Maternal Mortality Rates
Maternal mortality rates serve as a critical indicator of a nation’s overall health and wellbeing. In the U.S., the persistent rise in these rates is a clear signal of failing health policies, particularly regarding care for racial and ethnic minorities. Studies reveal that, over the years, cardiovascular diseases have emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, a shift that reflects increasing prevalence of chronic conditions like hypertension among younger populations. This change necessitates a reevaluation of how maternal health is approached, prioritizing disease prevention and management before, during, and after pregnancy.
The implications of high maternal mortality rates extend beyond individual tragedies; they reflect implicit societal biases and systemic inequities in healthcare access and treatment. There’s a critical need to advocate for policies that address these patterns of preventable deaths, particularly for vulnerable groups. Improved postpartum care and continued support for mothers beyond the immediate delivery period can play a crucial role in reversing this trend and ensuring that fewer lives are lost unnecessarily.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
Racial disparities in maternal health outcomes have been a persistent issue, exemplified by the significantly higher pregnancy-related death rates among Black and Indigenous women compared to their white counterparts. These disparities are often rooted in socio-economic factors, access to quality healthcare, and ongoing systemic racism within the medical community. Tackling these disparities requires a multi-faceted approach that includes community engagement, education on maternal health, and advocacy for equitable healthcare policies.
Recent studies have highlighted the urgent need for healthcare reform that addresses these racial inequities. Effective interventions may involve increasing accessibility to healthcare services, providing comprehensive maternal education programs, and fostering culturally competent care that respects and understands the unique challenges faced by diverse populations. By committing to these strategies, the healthcare system can work toward reducing racial disparities and ultimately saving lives in communities that have historically been underserved.
The Role of Postpartum Care in Reducing Maternal Deaths
Postpartum care plays a pivotal role in reducing maternal deaths and ensuring that new mothers are supported throughout their recovery. Research shows that a significant proportion of maternal deaths occur in the months following childbirth, highlighting the importance of continuous medical supervision and emotional support during the postpartum period. Implementing comprehensive postpartum care programs that follow women through the first year after delivery can greatly decrease the risk of preventable deaths.
Furthermore, postpartum care should be treated as an integral part of maternal health, extending beyond the traditional six-week check-in. By promoting regular follow-ups and providing education on warning signs of potential health issues, the healthcare system can help mitigate risks associated with complications such as hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. Addressing the postpartum phase with increased attention could lead to considerable improvements in maternal health outcomes.
COVID-19’s Influence on Maternal Mortality Trends
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted maternal health outcomes, with evidence suggesting that maternal mortality rates have worsened during this period. The initial disruptions to healthcare services during the pandemic not only compromised prenatal care but also limited access to essential postpartum services, contributing to an increase in pregnancy-related deaths. The sharp rise in mortality rates during 2021 illustrates how external public health emergencies can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities within maternal healthcare systems.
As healthcare systems recover from the pandemic, there’s a pressing need to address the lessons learned. Enhanced preparedness for future health crises is essential, as is a commitment to strengthening perinatal health services to prevent disruptions from negatively affecting maternal health. This includes integrating maternal care planning into broader public health strategies to ensure that the momentum gained in addressing maternal mortality does not wane.
Chronic Health Conditions and Pregnancy Risks
Chronic health conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, have an increasing impact on pregnancy-related outcomes. The alarming rise in hypertension and related disorders among younger women signals a concerning trend that could continue to worsen maternal health. Addressing these chronic conditions requires a proactive approach to women’s health that encompasses education, early intervention, and sustained healthcare support before and throughout pregnancy.
Furthermore, understanding the relationship between chronic disease management and maternal health is critical. Healthcare providers should focus on comprehensive assessments and tailored interventions that address individual health needs, particularly for women of reproductive age at higher risk. By integrating chronic disease management into maternal healthcare plans, the likelihood of adverse outcomes can significantly diminish.
State-Level Variations in Maternal Health Outcomes
Significant variations in maternal health outcomes across states reveal systematic failures and successes that inform policy development. For example, some states exhibit far lower pregnancy-related death rates than others, suggesting that best practices in maternal care are not universally adopted. By examining these discrepancies, policymakers can identify effective strategies and allocate resources more efficiently to improve maternal health nationwide.
Moreover, understanding why certain states excel in maternal health outcomes while others lag behind can provide valuable insights into the underlying structural issues within healthcare systems. This knowledge can pave the way for targeted interventions that address both high risk and low-performing states effectively. Collaborative efforts to standardize best practices across diverse healthcare landscapes are essential in the pursuit of eliminating preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure for Maternal Health
Investing in public health infrastructure is crucial for addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths. As financial resources for maternal health continue to face cuts, the risk of exacerbating existing disparities increases. Strengthening public health initiatives and reinforcing support systems for expectant mothers can lead to comprehensive improvements in healthcare delivery and outcomes. This necessitates a commitment from both state and federal levels to prioritize maternal health as a fundamental aspect of public welfare.
Additionally, the establishment of robust funding channels dedicated to maternal health research can facilitate innovations aimed at improving healthcare access and quality. By investing in community-based programs and preventive initiatives, stakeholders can collaboratively work towards shifting the focus from reactive to proactive care that ultimately enhances maternal and infant health outcomes.
Enhancing Healthcare Access for Pregnant Patients
Access to quality healthcare is a critical determinant of maternal health outcomes. Unfortunately, many pregnant individuals face barriers that prevent them from receiving the timely care they need. Factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and cultural stigmas often combine to create considerable obstacles. Addressing these barriers through policy reforms and community outreach initiatives is essential to ensure all women receive adequate prenatal and postpartum care.
Health systems must be redesigned to promote accessibility and equity, especially in underserved areas where maternity care deserts are prevalent. Strategies could include mobile health clinics, telemedicine services, and increasing the number of healthcare providers in high-need communities. By ensuring that every pregnant individual can access comprehensive support, the healthcare system can play a transformative role in reducing maternal mortality rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
In the U.S., cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of fatalities. Other significant causes include hemorrhage and severe complications from chronic conditions. This highlights the importance of addressing chronic diseases and improving postpartum care to prevent maternal mortality.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, with a troubling rise in pregnancy-related deaths over the past few years. Many of these deaths are preventable, emphasizing the need for enhanced prenatal care and addressing racial disparities in healthcare access.
What are the racial disparities in maternal mortality rates?
Racial disparities in pregnancy-related deaths are stark, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest mortality rates, followed by non-Hispanic Black women. These differences underscore the need for targeted interventions to address systemic inequities in healthcare.
How can postpartum care reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Improved postpartum care is crucial for reducing pregnancy-related deaths, as nearly a third occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Comprehensive care that extends beyond the initial postpartum period can help manage chronic conditions and monitor mothers’ health, ultimately preventing preventable deaths.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in maternal mortality?
Cardiovascular disease is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor to pregnancy-related deaths, affecting women at younger ages than before. Addressing chronic conditions like hypertension during pregnancy can help mitigate these risks and reduce maternal mortality rates.
What steps can be taken to address the increase in maternal mortality rates?
To combat rising pregnancy-related deaths, investments in public health infrastructure and innovative care solutions are needed. This includes enhancing the quality of care during pregnancy and postpartum, addressing policy discrepancies between states, and prioritizing maternal health in public health agendas.
Why is it important to include late maternal deaths in discussions about maternal mortality?
Including late maternal deaths—those occurring up to a year postpartum—in maternal mortality statistics is vital as it reflects the continuum of care needed in the postpartum period. Recognizing these deaths can lead to better healthcare systems that support women beyond the immediate weeks after childbirth.
What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic has likely exacerbated the rise in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly during 2021. This period highlighted the fragility of healthcare systems and the urgent need for improvements in prenatal and postpartum care to prevent further increases in maternal mortality.
How can policymakers help reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Policymakers can help reduce pregnancy-related deaths by implementing equitable health policies that address disparities, increasing funding for maternal health programs, and promoting best practices in prenatal and postpartum care, ultimately striving for improved health outcomes for all pregnant individuals.
What is the importance of tracking maternal deaths in the United States?
Tracking maternal deaths in the U.S. is essential for understanding the scope of maternal mortality and identifying areas for improvement. Accurate data collection, initiated in 2018 with a pregnancy checkbox on death certificates, allows for a clearer analysis of risks and outcomes, driving effective policy changes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates | U.S. pregnancy-related deaths continue to rise, with a maternal mortality rate of 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of these deaths are preventable, indicating a need for better healthcare systems and policies. |
| Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rates. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of cases. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly one-third of total deaths, highlighting a need for extended care. |
| Need for Investment | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative care solutions is critical to lower the pregnancy-related death rates. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the United States have reached alarming levels, with the nation having the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. The increase in deaths over the past years, particularly among vulnerable groups, underscores a critical need for improved maternal health care, equitable policies, and a comprehensive approach to prenatal and postpartum services. Addressing these issues is vital for reducing preventable deaths and ensuring that all mothers receive the care they deserve.